| distros | ||
| functions | ||
| img | ||
| tests | ||
| .dockerignore | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| CONTRIBUTING.md | ||
| CONTRIBUTORS.md | ||
| docker-bench-security.sh | ||
| docker-compose.yml | ||
| Dockerfile | ||
| functions_lib.sh | ||
| helper_lib.sh | ||
| LICENSE.md | ||
| MAINTAINERS | ||
| output_lib.sh | ||
| README.md | ||
Docker Bench for Security
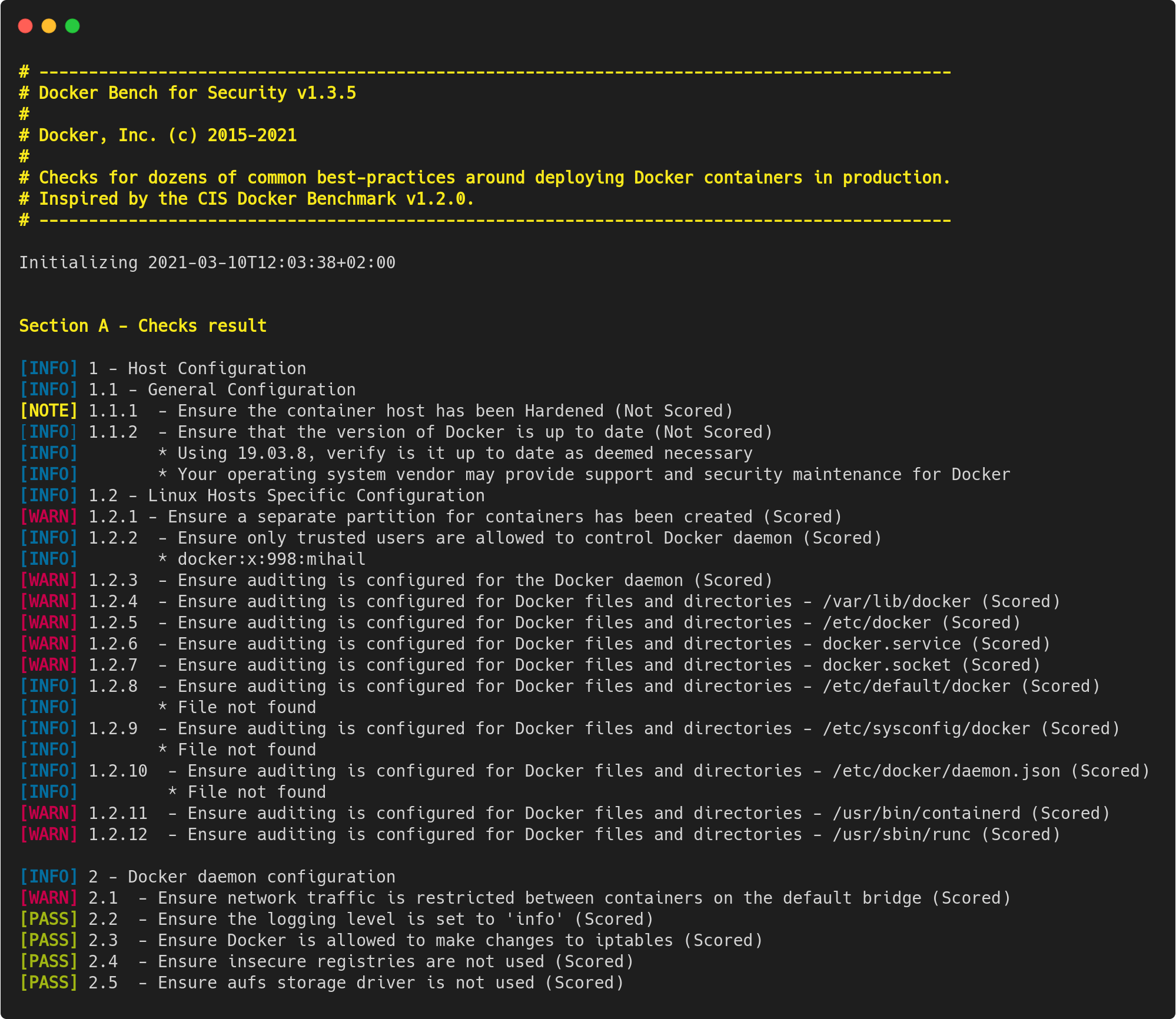
The Docker Bench for Security is a script that checks for dozens of common best-practices around deploying Docker containers in production. The tests are all automated, and are inspired by the CIS Docker Benchmark v1.2.0.
We are making this available as an open-source utility so the Docker community can have an easy way to self-assess their hosts and docker containers against this benchmark.
Running Docker Bench for Security
We packaged docker bench as a small container for your convenience. Note that this container is being run with a lot of privilege -- sharing the host's filesystem, pid and network namespaces, due to portions of the benchmark applying to the running host.
The easiest way to run your hosts against the Docker Bench for Security is by running our pre-built container:
docker run --rm --net host --pid host --userns host --cap-add audit_control \
-e DOCKER_CONTENT_TRUST=$DOCKER_CONTENT_TRUST \
-v /etc:/etc:ro \
-v /usr/bin/containerd:/usr/bin/containerd:ro \
-v /usr/bin/runc:/usr/bin/runc:ro \
-v /usr/lib/systemd:/usr/lib/systemd:ro \
-v /var/lib:/var/lib:ro \
-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock:ro \
--label docker_bench_security \
docker/docker-bench-security
Don't forget to adjust the shared volumes according to your operating system. Some examples are:
Docker Desktopon macOS doesn't have/usr/lib/systemdor the above Docker binaries.
docker run --rm --net host --pid host --userns host --cap-add audit_control \
-e DOCKER_CONTENT_TRUST=$DOCKER_CONTENT_TRUST \
-v /etc:/etc \
-v /var/lib:/var/lib:ro \
-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock:ro \
--label docker_bench_security \
docker/docker-bench-security
- On Ubuntu the
docker.serviceanddocker.secretfiles are located in/lib/systemd/systemfolder by default.
docker run --rm --net host --pid host --userns host --cap-add audit_control \
-e DOCKER_CONTENT_TRUST=$DOCKER_CONTENT_TRUST \
-v /etc:/etc:ro \
-v /lib/systemd/system:/lib/systemd/system:ro \
-v /usr/bin/containerd:/usr/bin/containerd:ro \
-v /usr/bin/runc:/usr/bin/runc:ro \
-v /usr/lib/systemd:/usr/lib/systemd:ro \
-v /var/lib:/var/lib:ro \
-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock:ro \
--label docker_bench_security \
docker/docker-bench-security
Docker bench requires Docker 1.13.0 or later in order to run.
Note that when distributions don't contain auditctl, the audit tests will
check /etc/audit/audit.rules to see if a rule is present instead.
Distribution specific Dockerfiles that fix these issues are available in the distros directory.
The distribution specific Dockerfiles may also help if the distribution you're using hasn't yet shipped Docker version 1.13.0 or later.
Docker Bench for Security options
-b optional Do not print colors
-h optional Print this help message
-l FILE optional Log output in FILE, inside container if run using docker
-c CHECK optional Comma delimited list of specific check(s)
-e CHECK optional Comma delimited list of specific check(s) to exclude
-i INCLUDE optional Comma delimited list of patterns within a container or image name to check
-x EXCLUDE optional Comma delimited list of patterns within a container or image name to exclude from check
-n LIMIT optional In JSON output, when reporting lists of items (containers, images, etc.), limit the number of reported items to LIMIT. Default 0 (no limit).
By default the Docker Bench for Security script will run all available CIS tests
and produce logs in the log folder from current directory, named docker-bench-security.sh.log.json
and docker-bench-security.sh.log.
If the docker container is used then the log files will be created inside the container. If you wish to access them from the host after the container has been run you will need to mount a volume for storing them in.
The CIS based checks are named check_<section>_<number>, e.g. check_2_6
and community contributed checks are named check_c_<number>.
A complete list of checks is present in functions_lib.sh.
sh docker-bench-security.sh -l /tmp/docker-bench-security.sh.log -c check_2_2
will only run check 2.2 Ensure the logging level is set to 'info'.
sh docker-bench-security.sh -l /tmp/docker-bench-security.sh.log -e check_2_2
will run all available checks except 2.2 Ensure the logging level is set to 'info'.
sh docker-bench-security.sh -l /tmp/docker-bench-security.sh.log -e docker_enterprise_configuration
will run all available checks except the docker_enterprise_configuration group
sh docker-bench-security.sh -l /tmp/docker-bench-security.sh.log -e docker_enterprise_configuration,check_2_2
will run all available checks except the docker_enterprise_configuration group
and 2.2 Ensure the logging level is set to 'info'
sh docker-bench-security.sh -l /tmp/docker-bench-security.sh.log -c container_images -e check_4_5
will run just the container_images checks except
4.5 Ensure Content trust for Docker is Enabled
Note that when submitting checks, provide information why it is a reasonable test to add and please include some kind of official documentation verifying that information.
Building Docker Bench for Security
If you wish to build and run this container yourself, you can follow the following steps:
git clone https://github.com/docker/docker-bench-security.git
cd docker-bench-security
docker build --no-cache -t docker-bench-security .
followed by an appropriate docker run command as stated above
or use Docker Compose:
git clone https://github.com/docker/docker-bench-security.git
cd docker-bench-security
docker-compose run --rm docker-bench-security
Also, this script can also be simply run from your base host by running:
git clone https://github.com/docker/docker-bench-security.git
cd docker-bench-security
sudo sh docker-bench-security.sh
This script was built to be POSIX 2004 compliant, so it should be portable across any Unix platform.